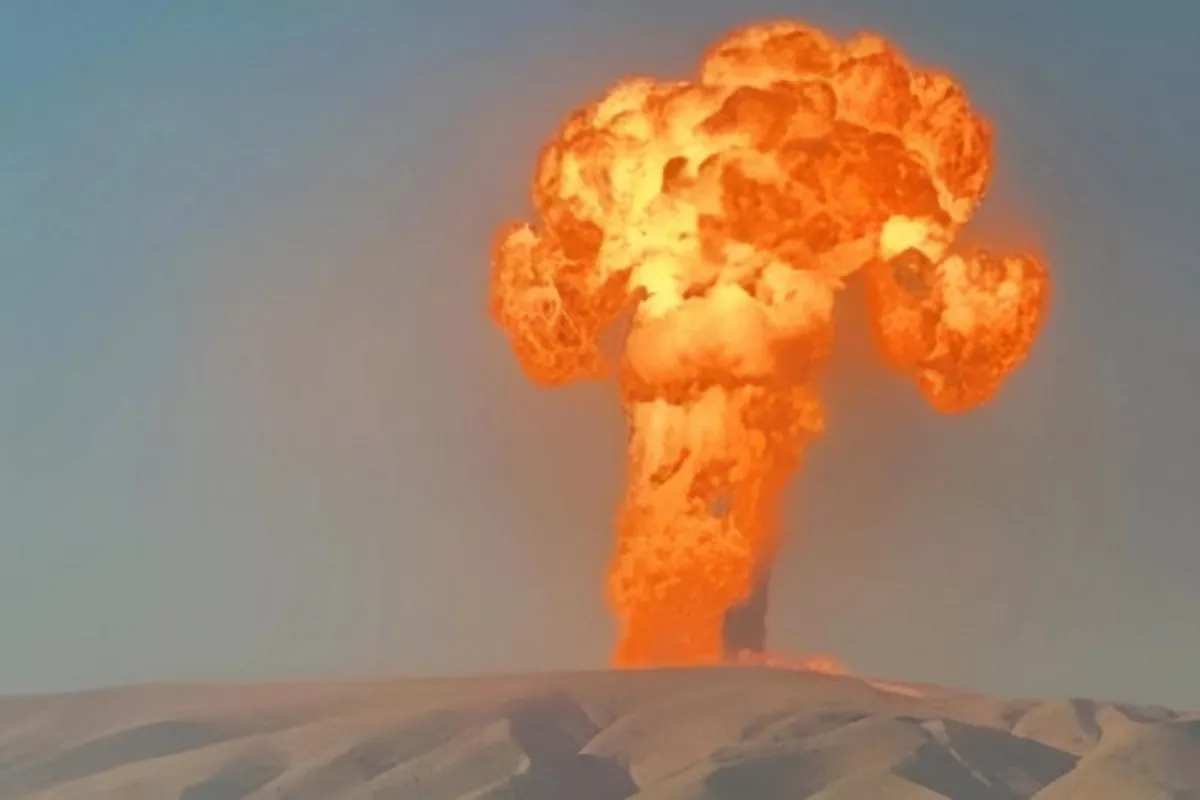
Photo: Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences
Azerbaijan has experienced one of the most powerful mud volcano eruptions in recent years in the Gobustan geological region, emphasizing the country's globally significant mud volcanism activity.
The Durandag mud volcano, known for its periodic activity, entered a new eruption phase, producing a powerful outburst that lasted about 15 minutes. During the peak activity, observers reported a flame column rising hundreds of meters into the air, while large volumes of mud breccia were expelled onto the surrounding land surface, The Caspian Post reports, citing the Azerbaijan National Academy of Sciences.
Scientific teams, along with specialists from the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources, conducted field monitoring to assess the scale and impact of the eruption. Researchers found that although the most intense phase was relatively short, strong combustion processes continued at the eruption center.
The ignition triggered a wide fire zone along the volcano’s eastern slope and in nearby vegetation areas. Experts say such fires can occur when flammable gases released during eruptions ignite upon contact with oxygen.
Preliminary research estimates show that the average thickness of mud deposits on the ground reached approximately 0.9 meters. The total affected area is estimated at around 14 hectares, while the total volume of expelled mud is believed to be about 126,000 cubic meters.
The eruption also caused significant structural damage within the volcanic zone. Scientists observed numerous radial cracks stretching for kilometers along the northern and southern edges of the mud flow area, indicating strong underground pressure release during the eruption.
According to geological records, this event marks the seventh major eruption (paroxysm) of the Durandag mud volcano. Previous eruptions were recorded in 1960, 1968, 1986, 2001, 2004 and 2016, showing a long-term pattern of periodic activity.
Researchers are continuing field studies at the site. Rock and mud samples collected after the eruption are now undergoing detailed laboratory analysis to better understand the volcano’s composition, gas content and eruption dynamics.
Azerbaijan is home to nearly half of the world’s mud volcanoes, making such events important not only locally but also for global geological research. Scientists say studying eruptions like Durandag helps improve understanding of underground gas systems, tectonic activity and environmental risks associated with mud volcanism.
Share on social media